43
Annual financial statements
RLB Tirol AG does not have any derivative financial instruments in its trading book.
Derivative financial instruments are recognised at their fair values, with ‘fair value’ meaning the value of an item on a specified date.
For derivatives, the value is determined on the basis of the fair market value, which is the amount for which an asset could be exchanged,
or a liability settled, between knowledgeable, willing parties in an arm’s-length transaction. If quoted prices on active markets are available,
these are used for valuation purposes. In the case of financial instruments with no stock market price, we use internal measurement
models applying current market parameters, in particular the cash value method and the option price model.
RLB Tirol uses derivatives to hedge both market risks (in particular interest risks and fair-value hedge interest rate risk) and the interest
result for certain financial assets, liabilities and executory contracts. The underlying transactions are holdings of RLB’s own securities,
issues and promissory notes, registered bonds, term deposits at banks, customer deposits, customer borrowings and derivatives. The
hedging transactions are interest rate swaps, forward rate agreements and interest rate options.
In the financial year 2014, obligations for close-out netting agreements were posted in the amount of 602,459 euros under other operating
costs.
The aim of these activities is to reduce income volatility. Derivative transactions not offset by proven hedging mechanisms should be
valued by application of the imparity principle. A proven micro-hedging relationship allows the simultaneous recognition of counteracting
effects in the underlying transaction.
The effectiveness of the various hedging interrelationships is measured chiefly by demonstrating the counteraction of key parameters
of the underlying and hedging transactions. This critical term match constitutes evidence of effectiveness both prospectively and
retrospectively. For the remaining exposures, this is done by matching the basis point values. By effectiveness in this context we mean the
relationship between the change as a result of hedging the underlying in the cash value (of that underlying) and the change in the cash
value of the derivative used for hedging purposes. RLB Tirol only recognises hedging relationships as such if they are likely to become
effective during their entire term.
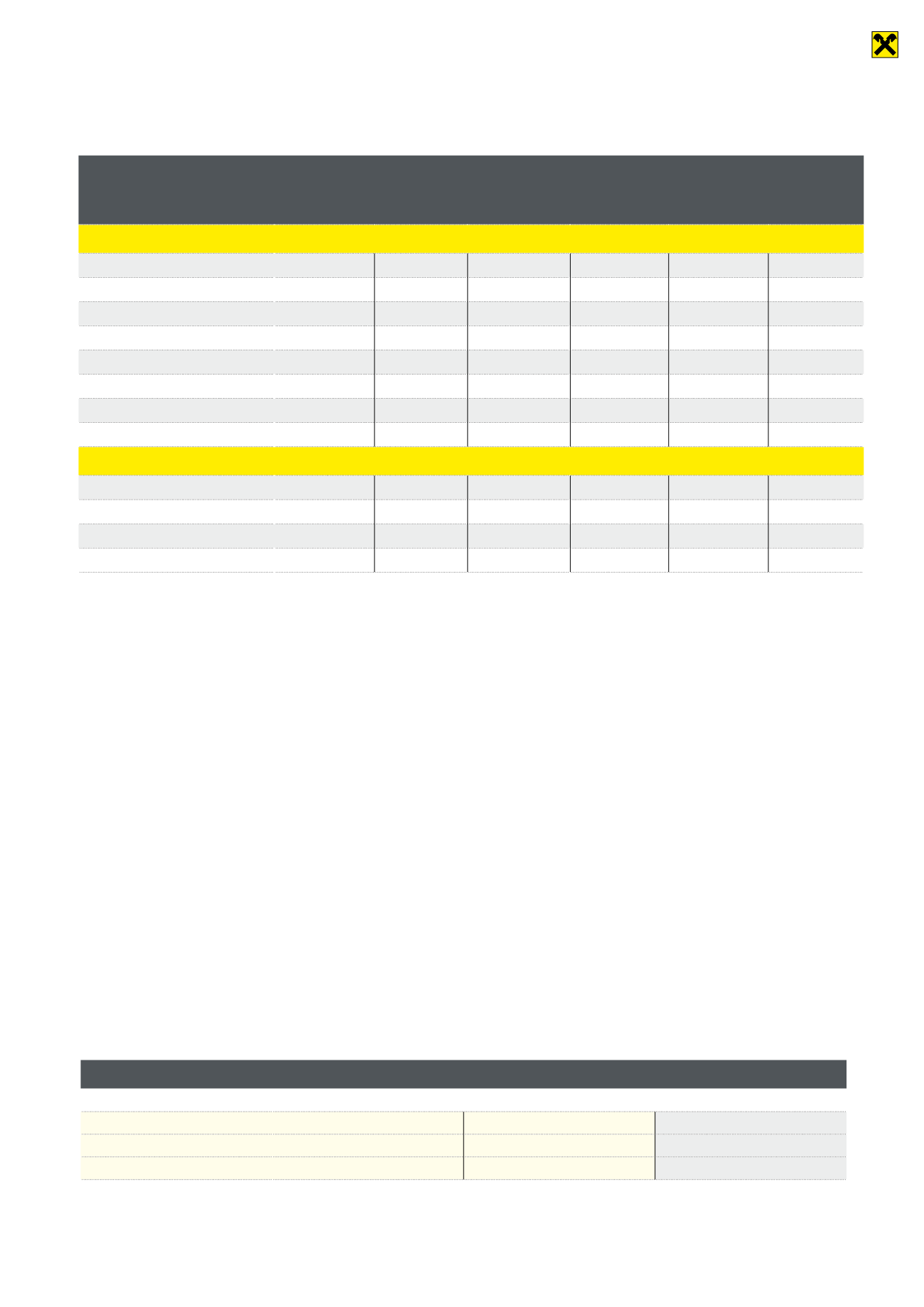
As of the balance sheet date, we held the following derivative financial instruments (in thousands of euros):
Category and type
Banking
book
Remaining terms of nominal values Market val-
ue, positive
Market
value,
negative
Up to 1 year 1 to 5 years More than 5
years
Interest rate derivatives
Interest rate swaps
4,558,872
648,817
1,705,096
2,204,959
177,464
343,726
Previous year
5,089,351
1,067,894
1,938,268
2,083,189
139,836
211,011
Interest rate futures – sale
0
0
0
0
0
0
Previous year
0
0
0
0
0
0
Interest rate options – purchase
240,209
1,189
136,680
102,340
7,363
305
Previous year
288,845
32,000
14,935
241,910
8,741
237
Interest rate options – sale
274,332
1,189
173,767
99,376
528
8,958
Previous year
315,168
32,000
44,836
238,332
376
9,260
Exchange rate derivatives
Currency futures
464
464
0
0
8
11
Previous year
302
302
0
0
0
0
Currency and interest rate swaps
1,238,546
348,747
414,697
475,102
8,992
19,345
Previous year
1,230,569
304,220
407,257
519,092
10,298
59,272
During the financial year, a provision of 3,060,000 euros was formed for open interest rate swaps (previous year: 1,290,000 euros).
Hedge derivatives
Fair value Negative market value
In euros
In euros
Cap floor
–1,370,719
–9,262,336
Swaps
–166,892,853
–311,132,874
Total
–168,263,572
–320,395,210


